











InHappiness Foundation SOWETO, SOUTH AFRICA (NON-PROFIT COMPANY REG. 2013/087817/08)
Happiness University FREE OPEN UNIVERSITY, International Happiness Institute INC., WASHINGTON DC
HAPPINESS UNIVERSITY NO MEDICAL ADVICE TERMS OF USE PRIVACY POLICY TRADEMARKS











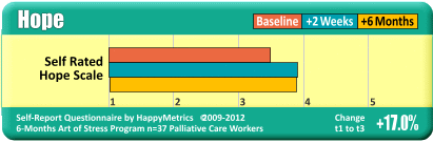

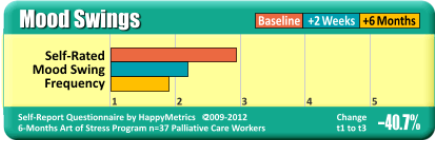
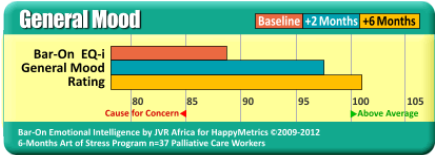

Positivity, Optimism, Happiness, General Mood, Mood Swings,
Hopefulness, Joyfulness.
Results shown are from a USAID funded study to determine the efficacy of an InHappiness laughter-assisted behavior change program in a highly stressed group of healthcare workers providing care to adults and children infected/affected by HIV and AIDS. Baseline results were taken before the program started and again periodically over six months. These results from detailed and validated measures are in keeping with results from hundreds of other highly- stressed groups. For more information see “Why are these results important?” below.








Real Results: Page One

Why are these Results Important?
•
Positivity is a reliable indicator of individual and team performance.
Increases in positivity boost productivity (Edge, 2013), widen the scope of
attention (Fredrickson & Branigan, 2005; Rowe, Hirsch, & Anderson, 2005), broaden
behavioral repertoires (Fredrickson & Branigan, 2005), increase intuition (Bolte,
Goschkey, & Kuhl, 2003) and creativity (Isen, Daubman, & Nowicki, 1987), improve
health (Fredrickson, Mancuso, Branigan, & Tugade, 2000) and immune function (Davidson
et al., 2003), increase resilience to adversity (Fredrickson, Tugade, Waugh, & Larkin,
2003), happiness (Fredrickson & Joiner, 2002), psychological growth (Fredrickson et al.,
2003), leadership effectiveness (Norman, Avolio, Luthans, 2010), and significantly
reduce stress (Steptoe, Wardle, & Marmot, 2005). For more about the benefits of
positivity in the workplace see Fredrickson & Losada 2005, Wikipedia, and
PositivityRatio.com.
•
Optimism drives performance, job satisfaction, work happiness, and
organizational commitment (Youssef & Luthans, 2007). Optimistic managers boost
employee optimism, engagement, and project performance (Greenberg &
Arakawa , 2006).
•
Happiness - Happy people are more successful in all areas of life.
They are more likely to be employed, more likely to be promoted, receive
better evaluations from supervisors, less likely to lose their jobs, and
generally earn more money. They are better organizational citizens, have
more friends and stronger social support networks, enjoy better health, have
lower levels of stress and depression, are judged as more physically
attractive , more intelligent and competent, more friendly, warm, and
assertive, and less selfish.
Happy teams experience less conflict and greater cooperation, and are
better at coping with stress, change, and unexpected difficulties. They are
more creative and innovative and better at solving problems (Lyubomirsky,
Diener, & King, 2005).
Happy brains are 31% more productive, happy sales people sell 37% more,
and happiness activates the brain’s learning center for faster learning and
better retention (Achor, 2010).
•
Mood — Mood disorders are important causes of productivity loss (NIMH).
Happy moods make people appear more appealing and inviting to possible
interaction partners (Veenhoven, 1988). Mood disorders are estimated to cost
more than $50 billion per year in lost productivity and result in 321.2 million
lost workdays (Kessler et al., 2006).
•
Hopefulness drives performance, job satisfaction, work happiness, and
organizational commitment (Youssef & Luthans, 2007). Lack of hope can drive
depression and even suicidal behavior (Beck et al., 1985).
•
Joyfulness is a major contributor towards happiness, productivity, and
workplace performance (Clements-Croome, 2000; Reio & Ghosh, 2009).


























Read about the Study
This study was documented in the book Healing with Happiness now available on Amazon.com.

